Collecting Plate and Discharge Electrode
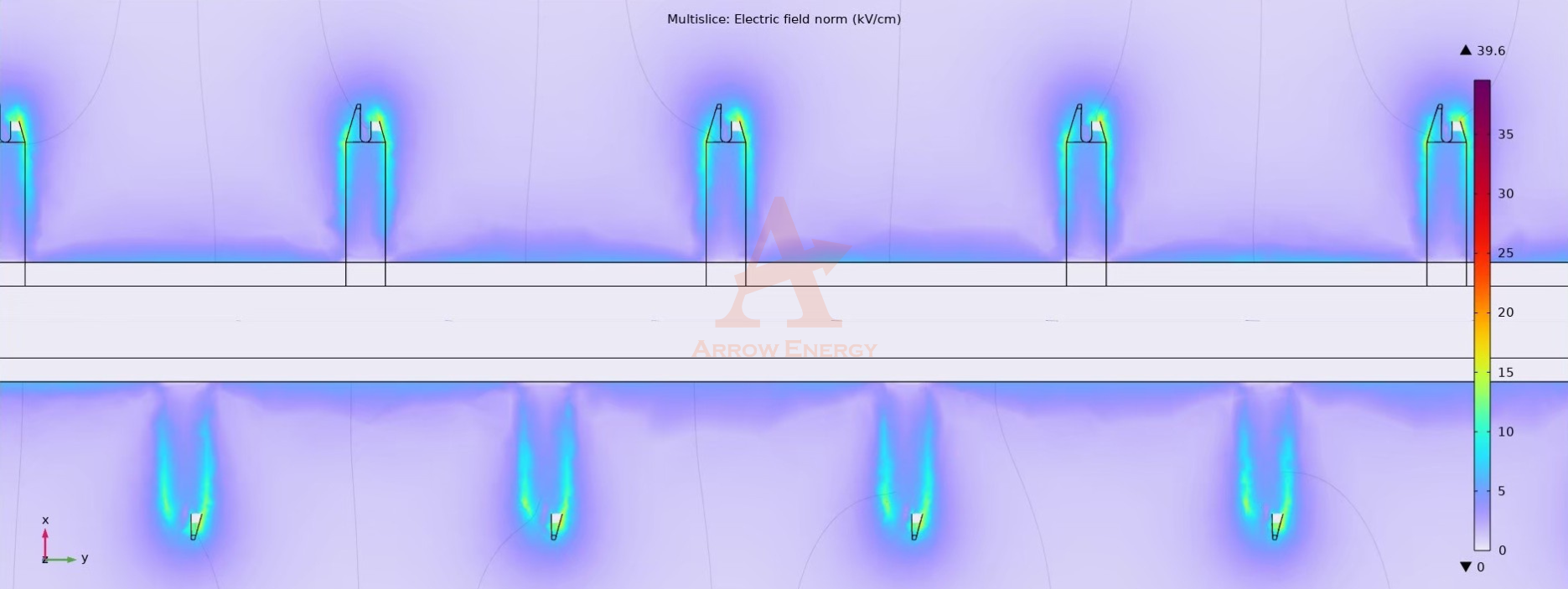
Collecting Plates: Capturing the Charged Particles
- Electrostatic Attraction:
- The collecting plates are flat, metallic surfaces placed parallel to the discharge electrodes.
- These plates are oppositely charged (usually positive) relative to the charged particles.
- The charged particles are attracted to the plates and adhere to them due to electrostatic forces.
- Particle Accumulation:
- Over time, a layer of particulate matter accumulates on the plates.
- Regular cleaning prevents this buildup from reducing collection efficiency.


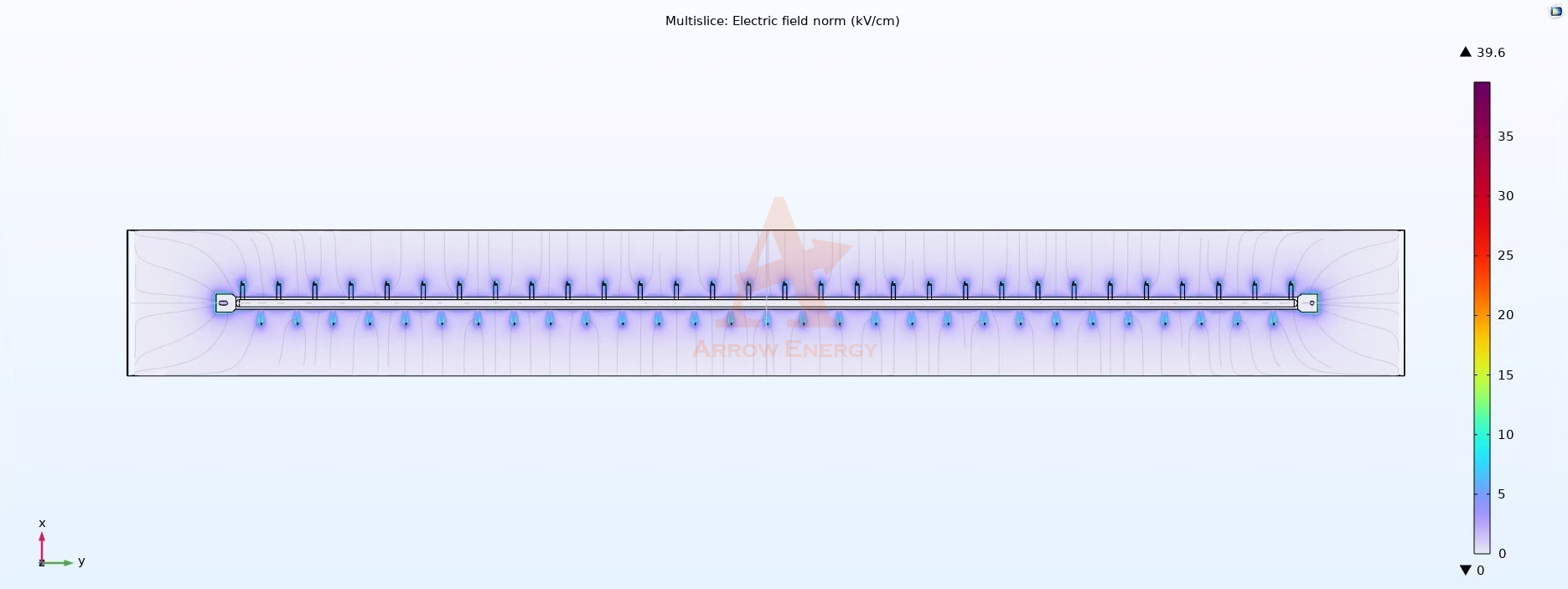
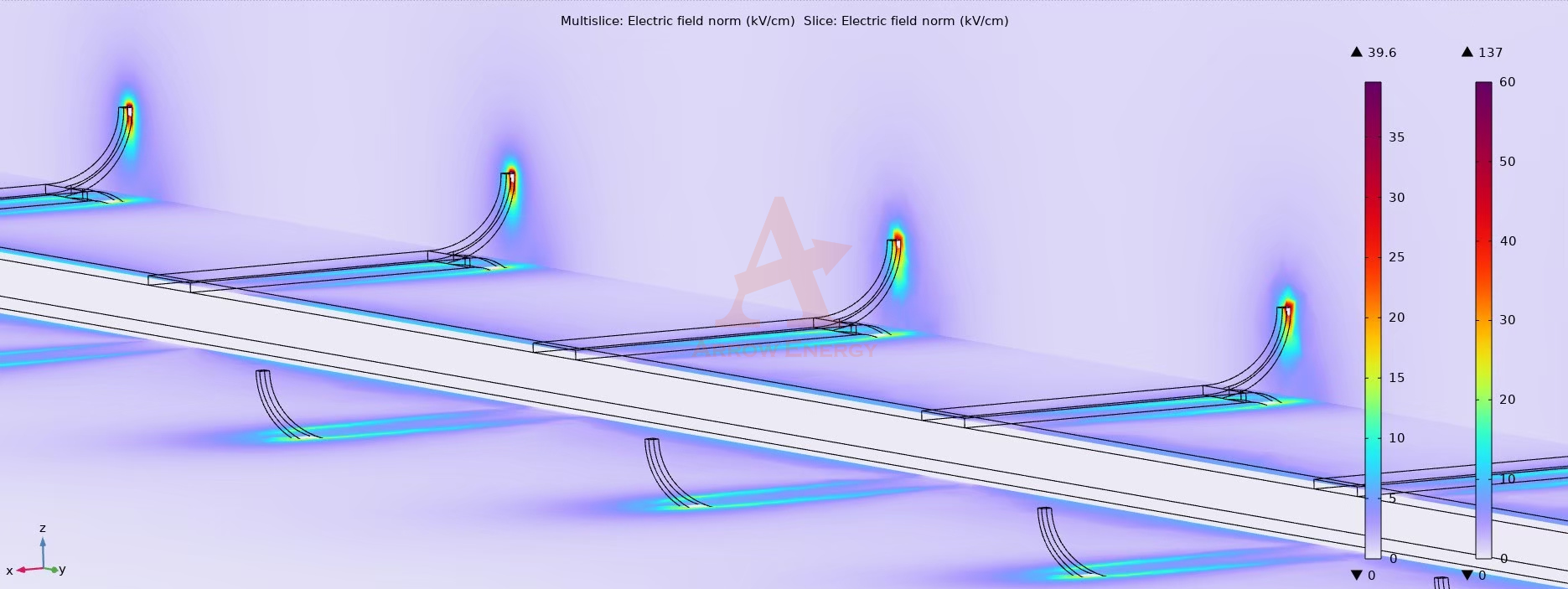
Discharge Electrodes: Ionizing the Particles
- Corona Discharge Generation:
- The discharge electrodes are thin, wire-like structures connected to a high-voltage power source.
- These electrodes produce a corona discharge, which generates a strong electric field and releases ions into the surrounding space.
- Particle Ionization:
- When dust-laden gas flows through the ESP, the particles are exposed to the electric field.
- The particles interact with the ions, acquiring a negative or positive charge, depending on the electrode’s polarity.
- Field Uniformity:
- The precise placement of discharge electrodes ensures the electrical field is evenly distributed, enabling consistent particle charging across the gas stream.
- High Efficiency: Plates and electrodes are engineered for superior particle capture.
- Durable Materials: Designed with high-alloy materials to withstand harsh operating conditions.
- Precision Charging: Ensures minimal energy loss and maximum collection efficiency.
